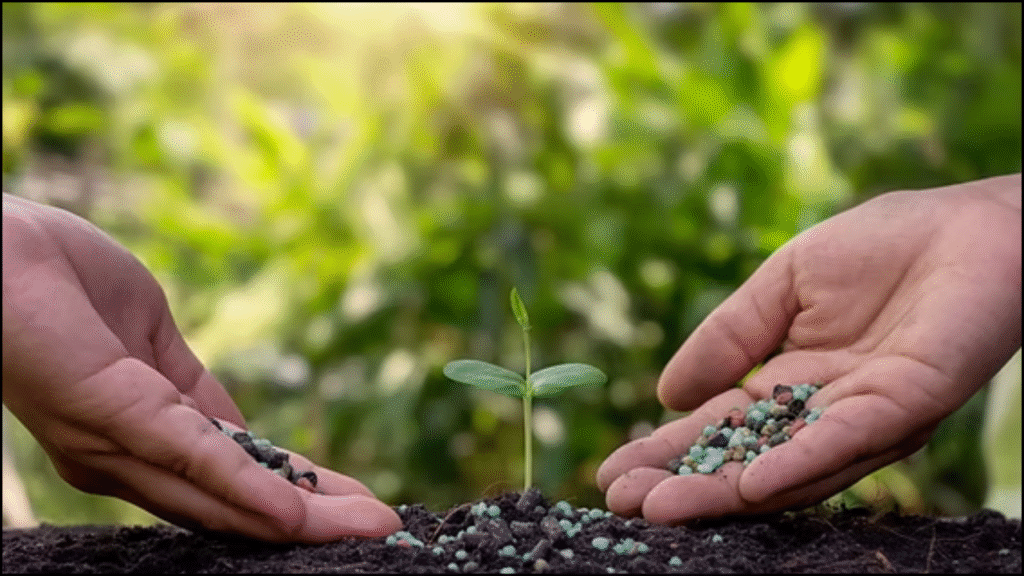
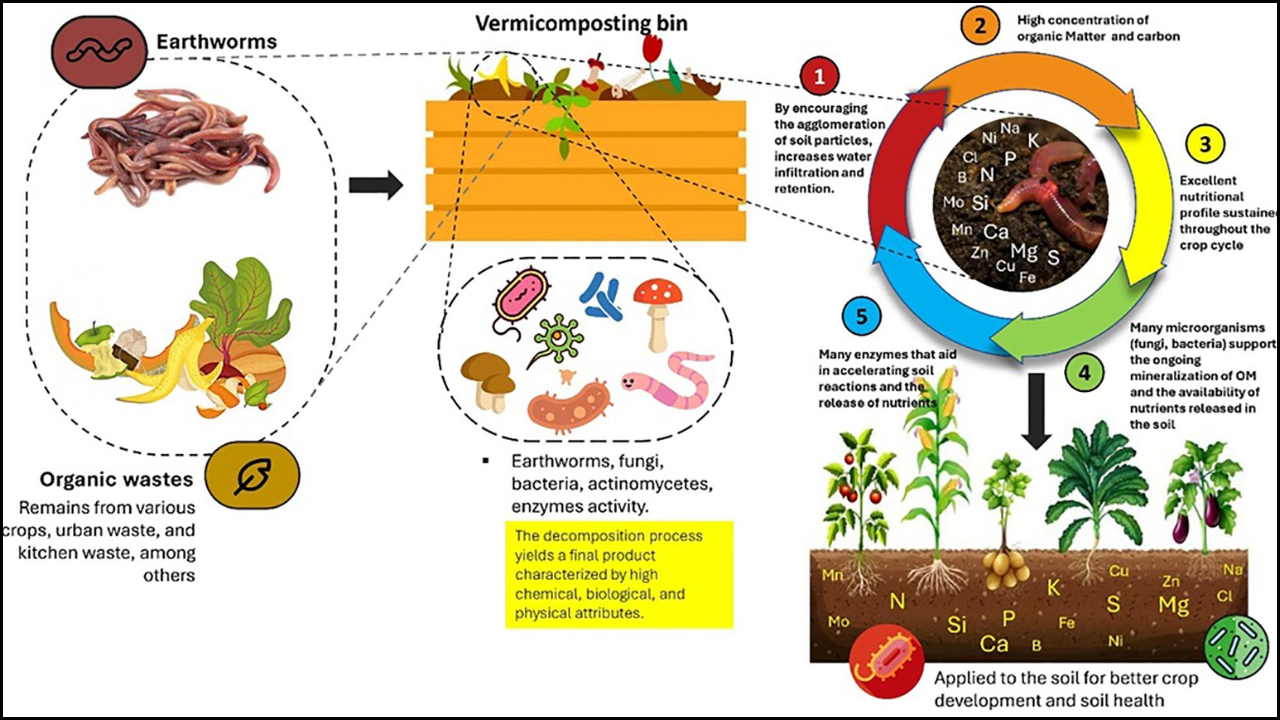
Fertilizers are vital for boosting agricultural productivity, but their overuse or misuse can harm both the environment and farmers’ finances. Today, improving fertilizer use efficiency (FUE)—the ability of plants to absorb and utilize nutrients effectively—has become essential. By applying the right type of fertilizer, at the right rate, time, and place, farmers can achieve higher yields while reducing waste, lowering input costs, and maintaining long-term soil health.
Table of Contents
Understanding Fertilizer Use Efficiency
Fertilizer use efficiency measures how effectively crops take up and use nutrients provided through fertilizers. A high FUE means that most of the applied nutrients are absorbed by the plants, while a low FUE indicates losses through leaching, volatilization, or runoff. When fertilizers are not efficiently used, they not only fail to support plant growth but also cause soil degradation and water pollution.
The goal of improving FUE is to balance productivity with sustainability. Farmers can achieve this balance by tailoring fertilizer practices to crop needs, soil type, and climatic conditions. The concept aligns closely with the 4R Nutrient Stewardship principle: using the Right source, Right rate, Right time, and Right place for fertilizer application.
The Importance of Proper Fertilizer Management
Fertilizer mismanagement—such as applying excessive amounts or using unsuitable nutrient types—leads to diminishing returns. While more fertilizer may boost yields initially, the long-term effects include nutrient imbalances, soil acidification, and reduced organic matter. Efficient fertilizer management ensures that plants receive nutrients in forms they can easily absorb, without harming the surrounding ecosystem.
By optimizing fertilizer use, farmers can also reduce their operational expenses. Fertilizers account for a major portion of agricultural costs, and applying them judiciously prevents financial losses due to overuse or poor timing. Moreover, maintaining soil health through proper fertilizer use ensures productivity for future growing seasons, rather than depleting the soil through short-term gains.
Optimizing Fertilizer Rates for Better Results
The correct fertilizer rate depends on the specific nutrient requirements of a crop, as well as the fertility status of the soil. Soil testing is one of the most effective ways to determine these needs. Applying fertilizer without knowing the soil’s nutrient content often leads to inefficiency—either by supplying too much of one nutrient or too little of another.
When farmers apply fertilizers based on scientific recommendations, crops receive balanced nutrition. For example, cereals like maize and rice need adequate nitrogen for growth, but excessive nitrogen can lead to lodging and lower grain quality. Combining soil tests with local agronomic knowledge allows farmers to fine-tune their fertilizer doses, ensuring both yield improvement and soil conservation.
Timing and Placement: Key to Efficiency
The timing of fertilizer application plays a major role in nutrient uptake. Applying fertilizers too early may result in nutrient losses through leaching or runoff before crops can absorb them. On the other hand, applying them too late may limit growth potential. Splitting fertilizer doses during critical growth stages ensures that nutrients are available when plants need them most.
Placement is equally important. Broadcasting fertilizers on the soil surface is common but often inefficient, as nutrients can evaporate or wash away. Techniques like band placement, where fertilizer is applied close to plant roots, or deep placement, which prevents nitrogen losses, are more effective. These methods enhance nutrient availability and minimize wastage.
Choosing the Right Type of Fertilizer
Different crops and soils respond differently to organic and inorganic fertilizers. Organic fertilizers such as compost, manure, or green manure improve soil structure, increase microbial activity, and enhance long-term fertility. Inorganic fertilizers provide specific nutrients in readily available forms, giving immediate results.
Integrating both types—known as Integrated Nutrient Management (INM)—can greatly improve fertilizer use efficiency. The organic component enhances soil health, while the inorganic part ensures quick nutrient supply. This balanced approach maintains soil productivity and reduces the environmental footprint of chemical fertilizers.
Benefits of Improving Fertilizer Efficiency
Enhancing fertilizer use efficiency benefits both farmers and the environment. Financially, it reduces input costs by minimizing unnecessary fertilizer purchases. Environmentally, it limits greenhouse gas emissions and nutrient runoff, which often lead to water contamination.
Soil health also improves when fertilizers are used efficiently. Balanced nutrient management promotes beneficial microorganisms, maintains soil pH, and preserves organic matter. Over time, these improvements contribute to resilient farming systems capable of sustaining productivity under variable weather conditions.
Modern Tools and Technology
Advances in precision agriculture have made fertilizer management more effective. Technologies such as soil sensors, drone mapping, and remote sensing allow farmers to monitor crop nutrient status in real time. Decision-support systems and smartphone applications also guide farmers in choosing correct fertilizer types and dosages, ensuring efficient resource use.
These innovations help bridge the gap between traditional farming methods and modern sustainability goals. They enable farmers to make informed decisions that optimize yields while conserving natural resources.
Conclusion
Fertilizer use efficiency is not only about saving costs—it’s about preserving soil health and ensuring sustainable food production. By adopting science-based practices in fertilizer selection, timing, and placement, farmers can maximize productivity while minimizing environmental harm. Improving efficiency is, therefore, a step toward a more sustainable and resilient agricultural future.
FAQs
Q1: What does fertilizer use efficiency mean?
It refers to how effectively crops absorb and utilize nutrients from applied fertilizers.
Q2: Why is efficient fertilizer use important?
It reduces costs, prevents soil degradation, and minimizes environmental pollution.
Q3: How can farmers improve fertilizer use efficiency?
By applying the right type, at the right rate, time, and place, based on soil testing and crop needs.