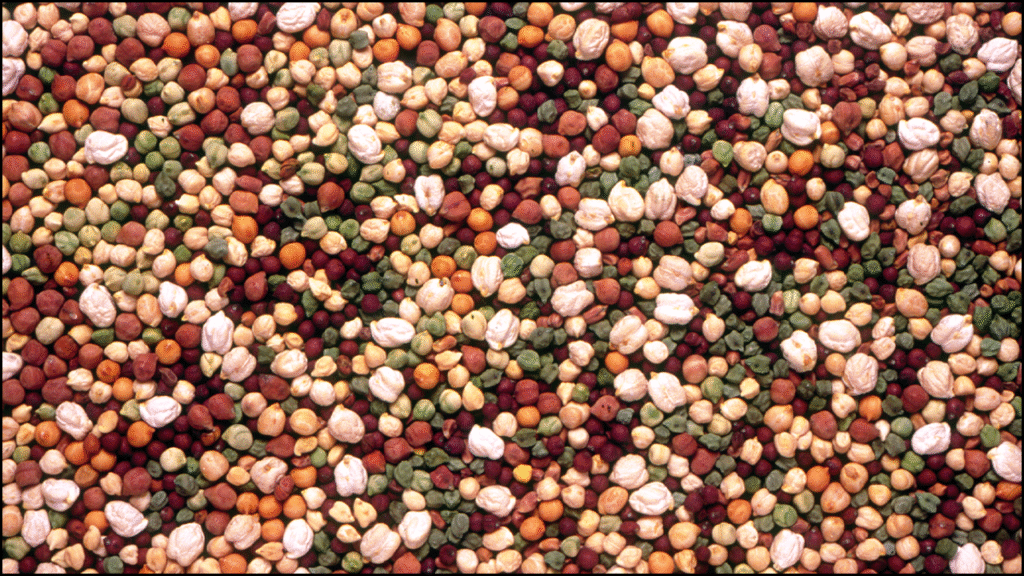
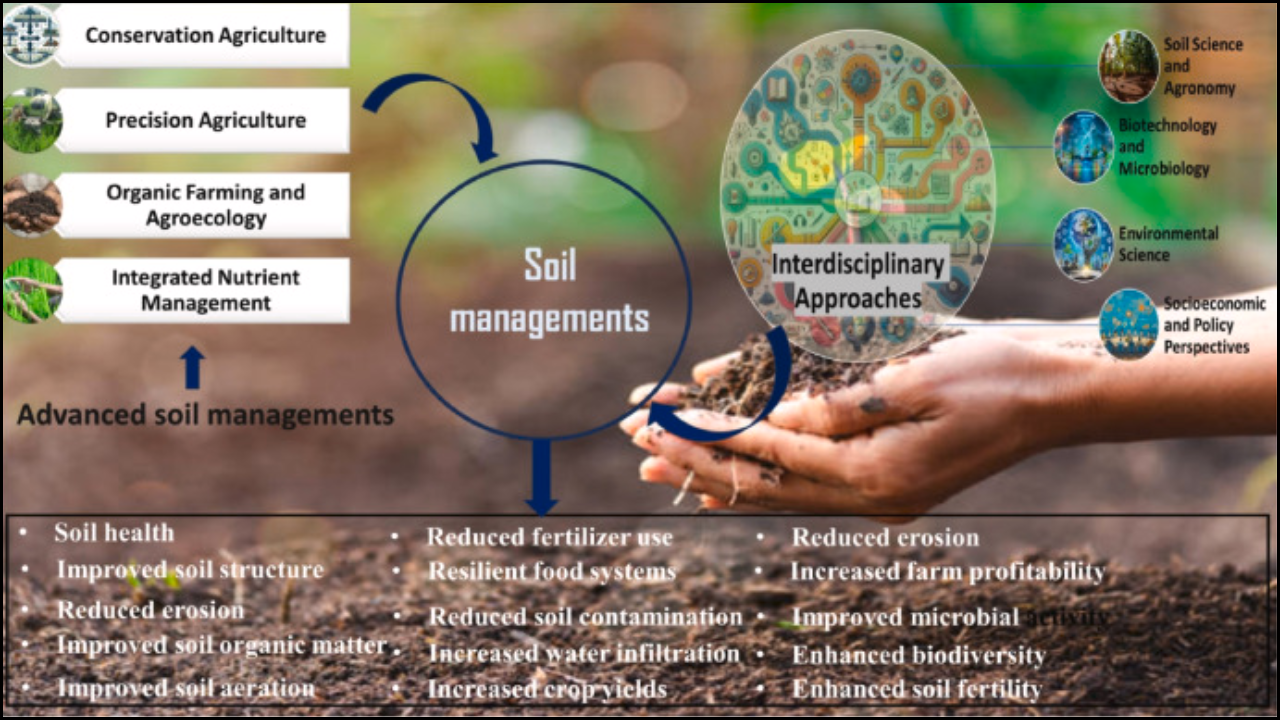
Chickpea holds a significant place in Turkey’s agricultural landscape due to its nutritional value, adaptability, and contribution to soil fertility through nitrogen fixation. Genetic diversity among Turkish chickpea varieties plays a vital role in improving yield, disease resistance, and environmental adaptability. Understanding this diversity allows breeders to develop improved cultivars suited for different climatic and soil conditions. A deeper assessment of genetic variability within local and improved varieties provides a foundation for enhancing the crop’s resilience and productivity.
Table of Contents
Importance Of Chickpea In Turkey
- Chickpea is one of the oldest cultivated legumes in the country.
- Turkey ranks among the top global producers of chickpea.
- The crop supports food security, income generation, and sustainable agriculture.
- Chickpea grains serve as an essential protein source for both urban and rural populations.
- Its deep-rooted system contributes to soil structure improvement and nitrogen enrichment.
Objectives Of Studying Genetic Diversity
- Identify genetic variation among local and improved varieties.
- Evaluate resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses.
- Enhance breeding efficiency for yield, quality, and adaptability.
- Conserve genetic resources for future breeding programs.
- Promote sustainable production under changing climatic conditions.
Major Chickpea-Producing Regions In Turkey
| Region | Key Provinces | Dominant Varieties | Climatic Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Central Anatolia | Konya, Ankara, Yozgat | ILC 482, Sezenbey, Gökçe | Semi-arid, low rainfall, cold winters |
| Southeastern Anatolia | Şanlıurfa, Diyarbakır | Diyar 95, Akçin 91 | Hot and dry with low humidity |
| Mediterranean Region | Adana, Mersin, Antalya | Çağatay, Hasanbey | Mild winters, moderate rainfall |
| Aegean Region | İzmir, Manisa, Aydın | Işık 05, Azkan | Coastal climate with fertile soils |
| Eastern Anatolia | Elazığ, Erzurum | Aziziye 94 | Cold winters and shorter growing seasons |
Genetic Diversity Parameters
Genetic diversity in Turkish chickpea is studied using morphological, biochemical, and molecular markers such as RAPD, ISSR, and SSR. These parameters help identify relationships among cultivars and locate unique genetic traits for breeding.
| Parameter | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Morphological Traits | Includes plant height, pod number, seed size, and flowering time. | Helps identify visible genetic variation. |
| Biochemical Markers | Based on protein and enzyme profiling. | Detects metabolic diversity among varieties. |
| Molecular Markers | DNA-based markers such as SSR and SNP. | Provides precise genetic relationship mapping. |
Morphological Diversity In Turkish Chickpea Varieties
- Seed Size and Shape: Turkish chickpeas show wide variation from small desi types to large kabuli types.
- Flowering Duration: Early-flowering varieties like Gökçe adapt to short growing seasons, while late-flowering types thrive in moist regions.
- Plant Height: Varieties exhibit plant heights ranging between 30 cm to 60 cm, depending on genotype and environment.
- Pod and Seed Number: Improved cultivars show higher pod density, contributing to yield stability.
- Color Variation: Seeds range in color from beige to dark brown, linked with market preference and genetic background.
Molecular Marker Studies On Turkish Chickpea
- Use of Simple Sequence Repeats (SSR) has revealed high polymorphism among landraces.
- Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) studies indicate a broad genetic base in Turkish germplasm.
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) have been employed for mapping genes associated with drought and disease resistance.
- Genetic clustering shows that Turkish landraces are grouped based on their eco-geographical origins rather than morphological similarities.
Role Of Landraces In Genetic Diversity
- Landraces represent traditional cultivars maintained by farmers for generations.
- These accessions hold adaptive traits for drought tolerance, disease resistance, and poor soil conditions.
- Landraces such as Karakız, Sarı 98, and Er 99 serve as valuable sources of allelic diversity for breeding.
- Conservation of these varieties through gene banks and on-farm management is crucial for sustainable agriculture.
Breeding Implications Of Genetic Diversity
- Genetic diversity serves as the foundation for hybridization programs.
- Crosses between high-yielding and stress-tolerant genotypes produce superior hybrids.
- Improved Turkish chickpea varieties such as Gökçe, Çağatay, and Hasanbey have been developed using local genetic resources.
- Breeding goals include resistance to Ascochyta blight, drought, and heat stress, which are major constraints in chickpea production.
Environmental Adaptation And Resilience
- Turkish chickpeas thrive under diverse environmental conditions due to their broad genetic adaptability.
- Drought-tolerant varieties perform well in arid zones of Central Anatolia and Southeast Turkey.
- Varieties adapted to low temperatures are cultivated in Eastern Anatolia.
- Improved genotypes have been developed to withstand salinity, temperature fluctuations, and pathogen attacks.
Contribution To Soil Health And Crop Rotation
- Chickpeas fix atmospheric nitrogen through symbiosis with Rhizobium bacteria.
- Rotational use of chickpea with cereals improves soil fertility and reduces pest incidence.
- Residual nitrogen benefits subsequent crops, minimizing fertilizer dependence.
- Integration with wheat and barley systems enhances resource efficiency and sustainability.
Challenges In Maintaining Genetic Diversity
| Challenge | Impact On Diversity | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Erosion | Loss of landraces due to preference for modern cultivars. | Promote in situ conservation programs. |
| Climate Change | Alters crop adaptability and stress responses. | Develop climate-resilient breeding lines. |
| Market Pressure | Uniform demand reduces genetic variability. | Encourage consumer awareness of traditional varieties. |
| Limited Germplasm Exchange | Restricts access to global genetic pools. | Strengthen international breeding collaborations. |
Technological Advances Supporting Genetic Diversity Studies
- Genomic Sequencing: Helps identify alleles responsible for stress tolerance and yield.
- Marker-Assisted Selection (MAS): Accelerates breeding by linking DNA markers with desired traits.
- CRISPR Gene Editing: Enables precise modification of genes for disease resistance.
- Bioinformatics Tools: Assist in analyzing large genetic datasets for variety improvement.
- Remote Sensing Applications: Monitor phenotypic expression and environmental interactions.
Economic And Agricultural Significance Of Diversity
- Genetic diversity underpins stable chickpea yields across varying environments.
- Diverse varieties ensure supply consistency despite climatic challenges.
- Enhanced resilience leads to lower production costs and higher farmer profitability.
- The export potential of Turkish chickpeas increases with improved quality traits and market adaptability.
Future Prospects For Turkish Chickpea Improvement
- Expansion of molecular breeding to combine high yield with resilience traits.
- Development of biofortified varieties with enhanced protein and micronutrient content.
- Strengthening gene bank collections and field conservation initiatives.
- Promotion of public-private partnerships in seed distribution and variety testing.
- Integration of climate-smart technologies to sustain productivity.
Wrapping Up
Genetic diversity within Turkish chickpea varieties forms the cornerstone of sustainable pulse production. The wide genetic base enables adaptability to varying environmental conditions and offers valuable traits for breeding superior cultivars. Effective conservation, advanced molecular tools, and collaborative research can strengthen chickpea improvement programs. A balanced focus on landrace preservation and modern breeding ensures the long-term resilience and productivity of chickpea cultivation in Turkey.